Study Trip:
Japan 4.0
Japan is a country known for its rich history, beautiful landscapes and fascinating culture. It is also a country that embraces innovation and is at the forefront of technological developments.
The Symbol Japan trip was an interesting travel experience that allowed participants to explore the splendor and culture of Japan. This unique trip brought people together to explore some of the country’s most iconic sights, attend traditional ceremonies and better understand Japan’s corporate culture.
The world is changing at a rapid pace, how is Japan dealing with the new industry?
Review of the Symbol study tour to Japan
The trip began with a flight to Tokyo, where participants were welcomed by a local guide and taken to the beautiful Shinagawa Prince Hotel. After getting to know each other and discussing the learning objectives of the trip, the adventure really began. A visit to the Dutch Embassy in Tokyo was on the program, where inspiring presentations were given on doing business in Japan and developments in Smart Industry/Industry 4.0. Participants gained insight into Japanese economic policy and were inspired by the speakers’ in-depth knowledge and expertise.
The trip continued to other fascinating companies, including AVEX Tado, Kuwana Factory, NTN Mie Works, Shin Nihon Kogyo and Mitsubishi Electric Nagoya Works. Each company visit allowed participants to see how Japanese organizations are embracing technologies such as robotics, automation and data analytics to improve their manufacturing processes. Local Senseis and production managers shared valuable insights on Lean methodologies and how they apply the principles of Industry 4.0 in their daily operations.
In addition to the focus on industry and technology, the trip also provided space for cultural exploration. Participants visited historic and iconic sites in Tokyo, Kyoto and Osaka, where they were able to enjoy the beautiful temples, gardens and unique cultural heritage of Japan. The visit to the Sake Museum even gave them a chance to taste a traditional Japanese beverage.
Shinkansen
One of the highlights of the trip was traveling by Bullet Train, the famous Shinkansen, from Tokyo to Nagoya. With breathtaking views of the iconic Mount Fuji, participants not only enjoyed the speed and punctuality of Japan’s transportation system, but were also able to experience the beauty of the landscape.
The Bullet Train is a part of Industry 4.0 in Japan because of its use of advanced technologies, digitization and automation. It uses advanced control systems, sensors and data analytics to optimize operational efficiency. Automated systems provide a seamless travel experience and advanced communication technologies support real-time data exchange. The Bullet Train is an example of how technology can improve efficiency and customer experience in the transportation industry.
Haneda Innovation City
Haneda offers not only shopping and dining experiences, but also research and development facilities, advanced medical centers and convention facilities. An autonomous bus and robotic dogs provide transportation and security for the complex.
Haneda collects data on movements of people, energy consumption and spaces, creating a digital replica of the complex, called a Digital Twin.
The data in this city will be visualized through“3D K-Field,” an infrastructure for three-dimensional spatial data, and shared with service users, providers and developers.
A major challenge in Japan is the shortage of doctors. Robotics is being considered as a possible solution. Robots can be used in healthcare, both for medical services and security tasks, such as robotic dogs for security. Moreover, robots can also be used for food delivery, which is another useful application.
Visit to Toyota Tecno Museum
Toyota’s development as a car manufacturer, from its origins as a loom manufacturer to its current status as a world leader in the automotive industry was discussed in detail during our visit in Nagoya. Within Toyota, Industry 4.0 has developed through continuous improvement and innovation in manufacturing processes.
Some examples of how Toyota is implementing Industry 4.0 include:
– Internet of Things (IoT): Toyota uses IoT to connect machines and equipment and collect real-time data. This enables them to monitor machine performance, predict maintenance needs and optimize production processes.
– Digitization and data analysis: Toyota uses advanced data analysis techniques to collect and analyze large amounts of production data. Through advanced algorithms, they can gain insights that help optimize processes, identify bottlenecks and make data-driven decisions.
– Augmented Reality (AR): Toyota is using augmented reality to transform online car sales. Through virtual showrooms and interactive configurators, customers can explore and customize vehicles in a digital environment. AR allows customers to visualize different Toyota models, colors and features, even virtually test drive them. This immersive experience helps customers make informed decisions and strengthens their connection to the product. By connecting the physical and digital worlds, Toyota is boosting online sales and providing excellent customer experiences.
– Quality Control: Lean and Six Sigma remain important pillars within Toyota. They use methods such as Kaizen (continuous improvement) and Just-in-Time to reduce waste and improve product quality using smart sensors and real-time data analysis.
Avex relies on Kaizen approach
Avex Inc. Technology, based in Nagoya, has been producing high-quality products for more than 70 years, including for the automotive sector (with sales of about 55 million). Toyota is a major customer of theirs. Avex management encourages a culture of transparency and openness. Employees are encouraged to be critical, something that does not come naturally within Japanese companies.
During the presentation, Avex’s director recounted the company’s development over the past 70 years. During the financial crisis in 2008, the company was hit hard. Instead of laying off employees en masse, Avex realized that their employees were their most important asset. They therefore invested a lot of time in the development of their employees. This led to significant growth in the following years, even during the corona crisis, taking the same approach. Within Avex, the Kaizen approach is highly developed. Kaizen is applied at all levels of the organization to solve problems and improve processes. Although Avex is facing a shrinking workforce, they are still able to attract and retain employees. The average age is remarkably low, about 35 years at the original plant and 26 years at the new plant.
Johan Cruijff and Industry 4.0 in Japan
We also visited Shinnihon Kogyo in Mie, Japan. Shinnihon engineers fully automatic assembly machines for major manufacturers such as Denso, Toyota, Avex and NTN. They are also the largest Asian manufacturer of ball bearings, founded 62 years ago. Participants had questions about Industry 4.0, including IoT.
The director of Shinnihon demonstrated the application of IoT in one of their machines. Here, different products can be produced side by side without changeovers. The machine recognizes the product and automatically adjusts the operations.
In addition to advanced techniques, we saw a simple example of visual management: three inverted coffee cups in different colors on a steel tube, indicating production progress.
We also raised questions about the alignment between education and business needs and the difference between current and former engineers.
During the presentations, the board’s openness about financial matters, challenges such as the shrinking workforce and the transition to electric vehicles stood out.
As for the connection to Johan Cruijff, years ago Shinnihon’s director was inspired by a Johan Cruijff Foundation in the Netherlands, where he saw three generations playing soccer. He founded the “VEERTIEN” initiative in Japan, with 20 youth teams promoting sports and teamwork, named after Johan Cruijff’s back number.
Mitsubishi Electric Corp wants to automate the world
Mitsubishi Electric’s goal is to “Automate the World. The company operates in various fields, including industrial automation, power systems, electronic devices and communications.
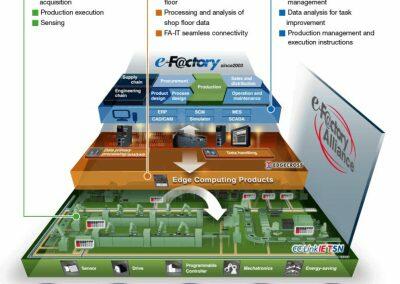
The future of manufacturing requires the realization of “Digital Manufacturing,” involving AI, 3D simulations, visualizations, data analysis, and so on. Mitsubishi Electric optimizes the entire manufacturing cycle (development, planning, production, recycling) using their approach called eFactory, which consists of three layers.
The first layer, “Shop floor,” focuses on engineering and supply chain improvement (productivity, quality, energy, safety and security). Mitsubishi provides controllers, servo motors, PLCs (Programmable Logic Controllers), HMIs (Human Machine Interfaces) and cobots to optimize production into the age of Industry 4.0.
The second layer, “Edge computing,” includes processing and analysis of primary production data and data management. This involves optimizing and filtering the large amount of process data generated by all machines and PLCs on the shop floor.
The third layer, “IT system,” includes all systems for automatically managing customer orders, product development support, planning and data management (ERP, CAD, SCM, MES and SCADA).
Register now for the Study Trip Japan 2024!
Are you ready for an extraordinary trip to Japan, the land of innovation, Kaizen and Industry 4.0? The Japan 2024 Study Trip awaits you and offers a unique opportunity to immerse yourself in the heart of Japanese business and culture.
Don’t miss this opportunity to be part of this incredible journey.
Register today to secure your place in this transformative adventure!
Also interesting to read
From Theory to Practice: Junior Consultant at Stoneridge
From theory to practice: Junior Consultant at Stoneridge Before working at Symbol, Junior Consultant Wisse Bos had never heard of a Production Part Approval Process (PPAP). Now he knows all the terms associated with a PPAP - such as PSW and PCN - like the back of his...
Optimize Quality Management with AI Tools
Optimize quality management with AI tools In the modern business environment, quality management is becoming increasingly important. Companies strive to provide high-quality products and services to ensure customer satisfaction and market competitiveness. Quality...
The Netherlands’ youngest Black Belt speaks
A ideal is not yet not a solutionEmiel recently gave a training session on the topic of problem definition and measurable requirements.During the session, he gave several times the feedback that it is not necessary, and may even be undesirable, to think about...